
#What is a router on a stick Pc#
Program to remotely Power On a PC over the internet using the Wake-on-LAN protocol. Also known as a one-armed router, it is the technique to allow. Sliding Window protocols Summary With Questions The Router on a stick is a method to transport multiple VLANs over a single router link. Router-on-a-stick is a type of router configuration in which you are able to use a single physical interface to route traffic between multiple VLANs. Sliding Window Protocol | Set 3 (Selective Repeat). A subinterface is created using the interface interfaceid.subinterfaceid global configuration mode command.  Sliding Window Protocol | Set 2 (Receiver Side) The router-on-a-stick method requires you to create a subinterface for each VLAN to be routed. Sliding Window Protocol | Set 1 (Sender Side). Controlled Access Protocols in Computer Network. Difference between Byte stuffing and Bit stuffing. Multiple Access Protocols in Computer Network. In the Router on a Stick configuration, the port is assigned multiple VLANs and called a trunk. The switch must be VLANd and normally on a VLANd switch port, the port is assigned to just one VLAN. ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam The Router on a Stick network uses one connection between the router and the switch. ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys. GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys. Consequently, the router subinterface approach can scale to a much larger number of VLANs than a configuration with one physical interface per VLAN design. This is the topology we’ll use: On the switch we have VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 and there’s only a single cable between the router and switch. Not only can this save money, it can also reduce configuration complexity. In this lesson, I’ll show you how you can use a router connected to a single switch as a router on a stick. Using trunk links and subinterfaces decreases the number of router and switch ports used. For PC1 to communicate with PC3, PC1 must have its data routed through router R1 via subinterfaces.Ĭlick the Play button in the figure to see how subinterfaces are used to route between VLANs. In the figure, PC1 wants to communicate with PC3. This way, the router can keep the traffic from each subinterface separated as it traverses the trunk link back to the switch.įunctionally, the router-on-a-stick model is the same as using the legacy inter-VLAN routing model, but instead of using the physical interfaces to perform the routing, subinterfaces of a single physical interface are used. Each subinterface is assigned an IP address specific to its subnet/VLAN and is also configured to tag frames for that VLAN. On the router, subinterfaces are created for each unique VLAN on the network. When configuring inter-VLAN routing using the router-on-a-stick model, the physical interface of the router must be connected to a trunk link on the adjacent switch. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0/1.3 192.168.3. This allows a single physical interface to simultaneously be part of multiple logical networks. Configure router on a stick To enable inter-VLAN communication, you can divide a single physical interface on a router into logical interfaces that will be. 4.2.8 Lab Configure Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN Routing Answers Lab Configure Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN Routing (Answers Version) Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only. Each subinterface is configured independently with its own IP address and subnet mask. Router on a Stick allows routing between VLANs with only one interface. Subinterfaces are software-based virtual interfaces that are assigned to physical interfaces. I am new to this concept and looking for some clarifications. This technique is termed router-on-a-stick and uses virtual subinterfaces on the router to overcome the hardware limitations based on physical router interfaces. I have set up a Router on a stick configuration with a Cisco 1841 router, a Cisco 2960 switch, and ESXi server.
Sliding Window Protocol | Set 2 (Receiver Side) The router-on-a-stick method requires you to create a subinterface for each VLAN to be routed. Sliding Window Protocol | Set 1 (Sender Side). Controlled Access Protocols in Computer Network. Difference between Byte stuffing and Bit stuffing. Multiple Access Protocols in Computer Network. In the Router on a Stick configuration, the port is assigned multiple VLANs and called a trunk. The switch must be VLANd and normally on a VLANd switch port, the port is assigned to just one VLAN. ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam The Router on a Stick network uses one connection between the router and the switch. ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys. GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys. Consequently, the router subinterface approach can scale to a much larger number of VLANs than a configuration with one physical interface per VLAN design. This is the topology we’ll use: On the switch we have VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 and there’s only a single cable between the router and switch. Not only can this save money, it can also reduce configuration complexity. In this lesson, I’ll show you how you can use a router connected to a single switch as a router on a stick. Using trunk links and subinterfaces decreases the number of router and switch ports used. For PC1 to communicate with PC3, PC1 must have its data routed through router R1 via subinterfaces.Ĭlick the Play button in the figure to see how subinterfaces are used to route between VLANs. In the figure, PC1 wants to communicate with PC3. This way, the router can keep the traffic from each subinterface separated as it traverses the trunk link back to the switch.įunctionally, the router-on-a-stick model is the same as using the legacy inter-VLAN routing model, but instead of using the physical interfaces to perform the routing, subinterfaces of a single physical interface are used. Each subinterface is assigned an IP address specific to its subnet/VLAN and is also configured to tag frames for that VLAN. On the router, subinterfaces are created for each unique VLAN on the network. When configuring inter-VLAN routing using the router-on-a-stick model, the physical interface of the router must be connected to a trunk link on the adjacent switch. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0/1.3 192.168.3. This allows a single physical interface to simultaneously be part of multiple logical networks. Configure router on a stick To enable inter-VLAN communication, you can divide a single physical interface on a router into logical interfaces that will be. 4.2.8 Lab Configure Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN Routing Answers Lab Configure Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN Routing (Answers Version) Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only. Each subinterface is configured independently with its own IP address and subnet mask. Router on a Stick allows routing between VLANs with only one interface. Subinterfaces are software-based virtual interfaces that are assigned to physical interfaces. I am new to this concept and looking for some clarifications. This technique is termed router-on-a-stick and uses virtual subinterfaces on the router to overcome the hardware limitations based on physical router interfaces. I have set up a Router on a stick configuration with a Cisco 1841 router, a Cisco 2960 switch, and ESXi server. 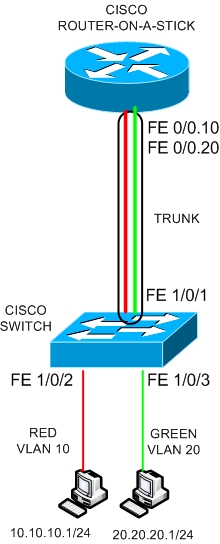
VLAN trunking allows a single physical router interface to route traffic for multiple VLANs. An alternative in larger networks is to use VLAN trunking and subinterfaces. Financially, it is more cost-effective to use subinterfaces over separate physical. Additionally, if you have a router with many physical interfaces, each interface is connected to a separate switch port, consuming extra switch ports on the network. As the number of VLANs increases on a network, having one physical router interface per VLAN quickly exhausts the physical interface capacity of a router. Routers that have many physical interfaces cost more than routers with a single interface. Routers have a limited number of physical interfaces to connect to different VLANs. Legacy inter-VLAN routing using physical interfaces has a significant limitation.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
